What is Manual Testing?
What is Manual Testing?
What is Manual Testing : When a software application is developed, it must be thoroughly tested to confirm that it works as expected. This includes verifying functional requirements (what the system should do) as well as non-functional requirements such as performance, usability, reliability, and security.
Software testing can be carried out in two main ways: manually or with the help of automation tools. When test cases are executed by a tester without using any automated tools, the process is known as Manual Testing. On the other hand, when testing activities are performed using specialized software tools, it is referred to as Automation Testing.
This tutorial focuses on Manual Testing. We will begin by understanding its formal definition, followed by the manual testing process, the importance of manual testing, and its limitations. We will also explore the various types of manual testing, share practical tips to become a better manual tester, and finally discuss some common misconceptions related to manual testing.
Manual Testing Process
Let’s examine the entire manual testing lifecycle to understand the different activities performed when testing an application.
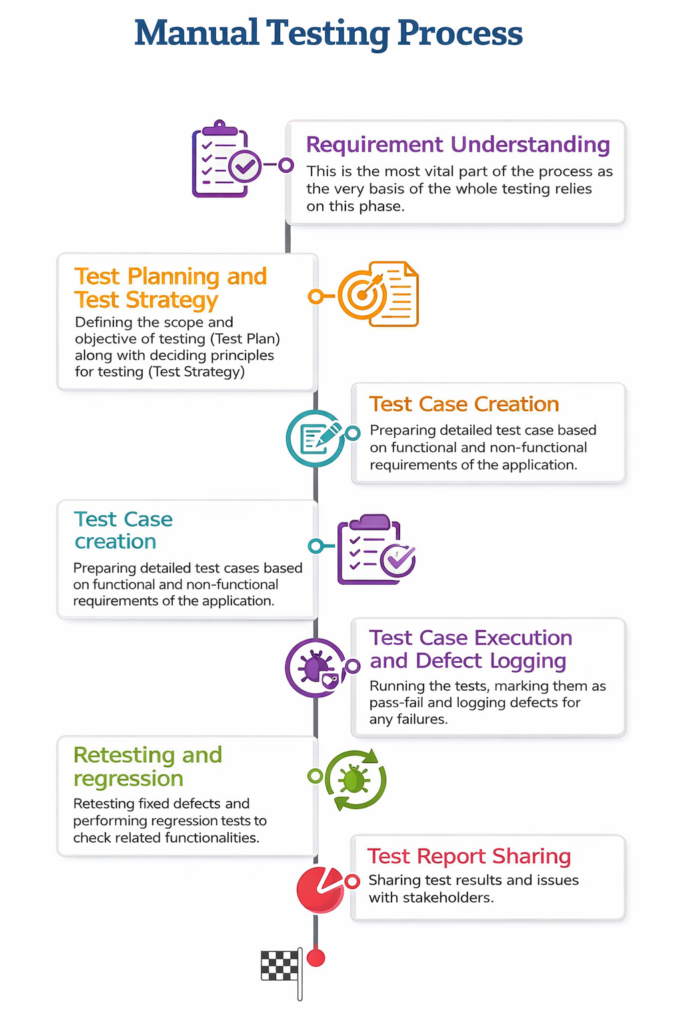
- 1. Requirement Understanding In this phase, all requirements are gathered and analyzed. This is the most critical phase of testing, as the requirements form the basis for test cases and the overall testing strategy.
- 2. Test Plan and Test Strategy During this phase, a Test Plan document is created to define the scope and objective of testing. Additionally, a Test Strategy is formulated to establish the principles and methods for how the testing will be carried out.
- 3. Test Case Creation After planning and strategy definition, we prepare test cases based on the functional and non-functional requirements of the application.
- 4. Test Case Execution and Defect Logging Once the test cases are ready and the application is available for testing, we begin executing the test cases. Each test case is marked as “Passed” or “Failed,” and defects are raised for every failure.
- 5. Retesting and Regression After developers fix the reported bugs, we perform retesting to verify the fixes. We also conduct regression testing to ensure that the changes haven’t adversely affected other existing functionalities.
- 6. Test Report Sharing Once the entire test execution cycle is complete, the test results—along with a list of known issues (if any)—are shared with the relevant stakeholders.
Advantages of Manual Testing
Let’s look at some of the key benefits:
- Maintains Quality: Manual testing helps find defects before delivery to the customer, thereby maintaining high application quality.
- Early Bug Identification: It aids in the early detection of bugs. Issues found by the customer or in the later stages of a project are difficult to fix and increase project costs. Efficient manual testing prevents this by catching issues early.
- Comprehensive Compliance: It ensures conformance not only to functional requirements but also to non-functional requirements such as performance, usability, and user-friendliness.
Disadvantages of Manual Testing
- Time-Consuming: It is a labor-intensive process, as testers must create exhaustive test cases and execute every step manually. Documenting the actual results also takes significant time.
- Resource Intensive: Compared to automation testing, manual testing typically requires more human resources to create and execute test cases.
- Prone to Human Error: Manual testing relies heavily on the skills and attention span of the tester. Even with predefined steps, two testers may report different results based on their individual understanding.
- Limitations on Scope: Certain types of testing—such as high-volume load testing, distributed testing, or complex multi-threaded operations—cannot be performed effectively without automation tools.
Tips for Better Manual Testing
To excel at manual testing, we have curated a list of qualities and habits that will help you become a better tester:
- Thorough Requirement Understanding: A correct and complete understanding of requirements is vital. It improves test coverage and the overall quality of testing.
- Good Domain Knowledge: Understanding the business domain is crucial. For example, a person with knowledge of the e-commerce domain can effectively test an e-commerce application even with a limited set of requirements, as they can anticipate unspecified user needs.
- Technical Skills: Skills such as database querying (SQL), understanding table structures, and knowledge of client-server architecture help testers understand the application’s internal data flow, leading to better test cases.
- Attention to Detail: Meticulous attention to detail ensures that every feature of the application is tested thoroughly.
- Do Not Assume: As testers gain experience, they may tend to take things for granted. However, no matter how simple or trivial a functionality seems, a tester should never assume it works without validation.
- Good Communication Skills: Testers deal with various stakeholders, including developers, managers, and clients. Good communication and interpersonal skills aid in the efficient gathering of requirements, as clearly articulated queries help avoid gaps in understanding.
Manual Testing Myths

Let us debunk some common myths surrounding manual testing.
Myth 1: Automation and AI will replace manual testing.
-
Fact: First, many types of testing, such as exploratory testing, usability testing, and ad-hoc UI testing, rely on human intuition and are best performed manually. Second, even for conventional testing, manual testing is required until the application becomes stable enough for automation scripts to be written. Since 100% automation is nearly impossible, manual testing is here to stay.
Myth 2: Testing starts only after development is completed.
-
-
Fact: Testing can start as early as the requirement elicitation phase. In many modern SDLC models, such as the V-Model, there is a corresponding testing activity for every development phase.
-
-
Fact: Efficient testing requires deep knowledge of the application, the domain, the database structure, and often the internal architecture. A tester must meticulously validate every aspect without assumption and clearly articulate complex issues to developers. It is a highly skilled profession.
Myth 4: Testing increases project cost.
-
Fact: The aim of testing is to ensure quality and detect bugs early. Bugs found in the early phases are significantly cheaper to fix than those found after delivery. In the long run, testing reduces the overall cost of the project by preventing expensive post-release failures.
Conclusion
In this post, we tried to cover the topic of manual testing. Right from its definition to its needs, limitations, tips, and myths. If you want to learn the different manual testing concepts then I strongly suggest our tutorial series on Software testing.
In this tutorial series, we have not only covered theoretical aspects of software testing but also provided practical resources like test cases of different scenarios, tutorials on testing different types of applications, etc.
Thanks!! Happy testing.
Most Asked Manual Testing Interview Questions for Freshers – 50+ Q&A
Important Links & Resources:
Follow our WhatsApp group: Click here
Follow Us on Instagram: Click here
Follow our Telegram Channel: Click here
