What Is Software Testing? An Easy Explanation For Beginners
What is Software Testing
What Is Software Testing : Human beings are prone to mistakes because of inattention, incorrect assumptions, carelessness, or inadequate system knowledge. This very nature of humans makes software vulnerable to bugs, defects, and errors (we will get to know these terms in detail in later posts). To prevent and correct these issues, we need testing.

Traditionally, software testing was done in a single phase, and that too only once the implementation or coding was completed. But the increasing complexity of software applications led to the evolution of testing.
So, testing techniques have evolved over time, and testing activities are no longer confined to a single phase. Instead, these are integrated with the different phases of the software development life cycle.
In this blog post, we will walk you through the nitty-gritty of software testing.
What is Software Testing?
Software testing is the process of evaluating a system with the intent of finding bugs. It is performed to check if the system satisfies its specified requirements and quality standards. It evaluates the system to validate its functionality.
Testing measures the system’s overall quality in terms of correctness, completeness, usability, performance, and other functional and non-functional attributes.
Software testing is not only associated with uncovering potential bugs or defects. It also involves finding measures to improve the system’s efficiency and accuracy.
Basically, software testing is the combination of verification and validation.
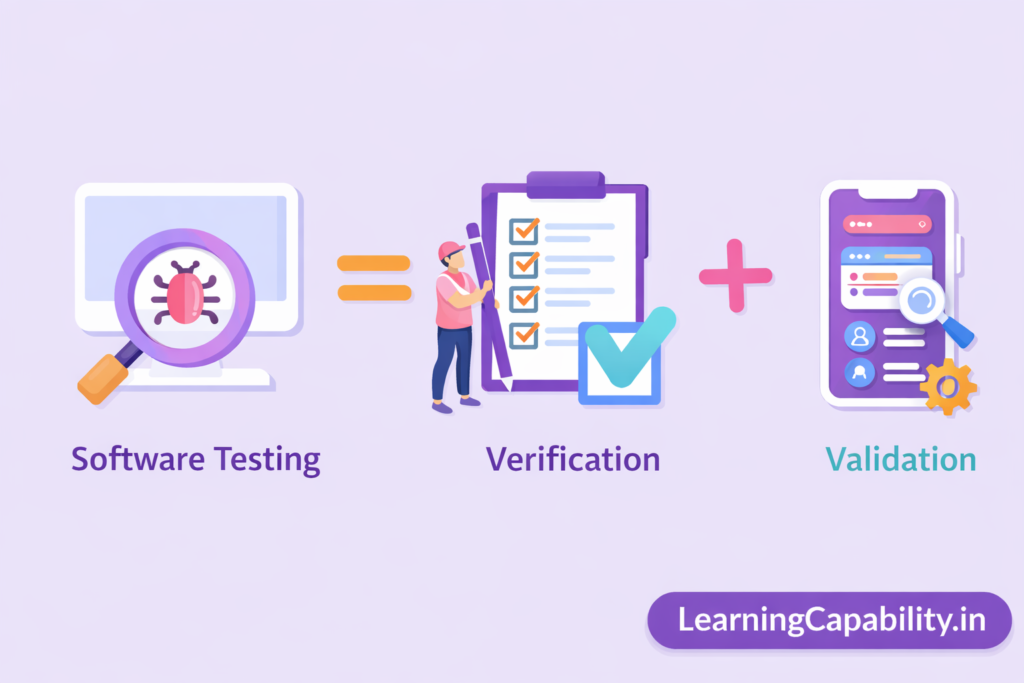
Verification
Verification is a static process that does not involve code execution. It validates documents, design, and code against specified requirements and answers the question:
“Are we building the product right?”
Validation
Validation is a dynamic process that involves code execution. It checks software for reliability, usability, and functionality. It answers the question:
“Are we building the right product?”
Why is Software Testing Important?
Software testing is an indispensable activity in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) because it helps identify defects early before the product reaches the end users.
Importance of Software Testing:
-
Provides assurance to stakeholders that the product works as intended
-
Prevents damage to company reputation due to faulty software
-
Builds confidence in product quality
-
Reduces cost by detecting defects early
-
Offers an independent perspective through the testing team
-
Prevents business failures caused by faulty software
-
Avoids life-threatening risks caused by software failures
Real-World Examples:
-
Starbucks’ POS system glitches caused 60% of stores in the US and Canada to shut down temporarily
-
F-35 fighter aircraft software bugs affected target detection
-
China Airlines Airbus A300 crash due to a software bug resulted in 264 deaths
-
Military satellite launch failure due to software bug cost $1.2 billion
-
A major US bank mistakenly credited $920 million to customers
Who Conducts Software Testing?
Software testing is performed by different stakeholders throughout the development process:
-
Developers – Conduct unit testing
-
Testers – Perform functional, performance, and automation testing
-
Test Managers/Leads/Architects – Define testing strategies and plans
-
End Users – Conduct User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
How is Software Testing Done? Types of Testing
Testing can be conducted manually or using automation tools.
Manual Testing
Manual testing involves executing test cases without automation tools. It includes:
- Requirement verification
- Test planning and strategy
- Test case creation and execution
- Defect reporting and retesting
- Test reporting
Manual testing focuses on understanding end-user behavior and identifying unexpected issues.
Automation Testing
Automation testing uses tools such as Selenium, Katalon Studio, and QTP to execute test scripts.
Benefits include:
- Faster execution
- Increased test coverage
- Improved accuracy
- Reduced time and cost
Functional Testing
Ensures the application behaves as expected.
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- System testing
- Acceptance testing
- Smoke testing
- Regression testing
- Sanity testing
Non-Functional Testing
Evaluates performance, security, and usability.
- Performance testing
- Load testing
- Stress testing
- Endurance testing
- Volume testing
- Security testing
- Recovery testing
Levels of Software Testing
1. Unit Testing
Tests individual modules or components, typically performed by developers.
2. Integration Testing
Verifies interaction between combined components.
3. System Testing
Tests the entire system against defined requirements.
4. Acceptance Testing
Ensures the system meets user expectations before release.
When Do We Start Software Testing?
Testing should begin early in the SDLC and can start even before development begins.
Mapping of Development and Testing Phases
| Development Phase | Testing Activity |
|---|---|
| Requirement Designing | Acceptance test creation |
| Functional Specification | Test case creation |
| Implementation/Coding | Unit test case creation |
| Code Complete | Test case execution |
When to Stop Testing?
Testing can be concluded based on:
- Required test case pass percentage achieved
- Successful completion of a full test cycle
- Deadlines met with no critical defects
- Acceptable Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF)
Challenges in Software Testing
Communication Issues
- Requirement misunderstandings
- Unclear documentation
- Poor collaboration
Resource Constraints
- Limited time and budget
- Skill and domain knowledge gaps
Change Management
- Frequent requirement changes
- Last-minute updates
Technical Challenges
- Unstable environments
- Compatibility across platforms
Best Practices in Software Testing
- Start testing early
- Define clear objectives
- Understand requirements thoroughly
- Use requirement traceability matrix
- Prioritize high-risk areas
- Test in production-like environments
- Review test cases regularly
- Promote continuous improvement
Conclusion
Software testing is a critical phase of software development that ensures quality, reliability, and performance. By identifying defects early and validating system functionality, testing helps deliver robust and user-friendly software products.
What is Manual Testing?
Important Links & Resources:
Follow our WhatsApp group: Click here
Follow Us on Instagram: Click here
Follow our Telegram Channel: Click here
